

What is thrombosis?
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a vein which can obstruct the flow of blood throughout the body. There are two types of thrombosis: phlebothrombosis and thrombophlebitis.
The first (phlebothrombosis) is the formation of a clot inside the vein, without inflammation but with a great capacity for detachment, given that it is poorly attached to the vessel wall. These types of blood clot usually affect the deeper venous system (deep vein thrombosis) and in bad cases can cause a stroke or a pulmonary embolism.
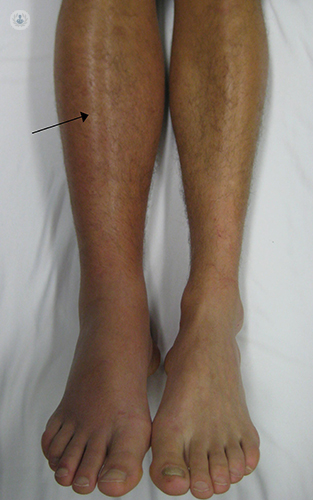
In the case of thrombophlebitis, the clot is usually attached to the venous wall and results in swelling, tenderness and redness in the affected area of the body. Thrombophlebitis commonly affects the smaller, superficial veins in your legs.
What are the symptoms of thrombosis?
The symptoms of phlebothrombosis are:
- Swelling
- Pain
- Can lead to a pulmonary embolism
The symptoms of thrombophlebitis are:
- Swelling and redness
- Some pain
What causes thrombosis?
Venous thrombosis is caused by either venous stasis (the slow movement of blood which can happen during long periods of immobility), hypercoagulability (an increased tendency for your blood to create clots due to an imbalance of clotting chemicals in the blood) or damage to the vein.
There are also certain risk factors that can increase chances of a blood clot forming:
- Older age
- Pregnancy
- Certain contraceptive pills
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Immobility (travel, hospital stays, injuries)
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Leg injury
- Major surgery
- Inherited blood disorders
- You have had previous blood clots
Can a thrombosis be prevented?
The emergence of a thrombosis can be prevented by controlling the normal fluidity of the bloodstream and preventing the formation of clots. Therefore, in certain cases such as those recovering from surgery or when a person is bedridden for a period, the administration of heparin or oral anticoagulants are recommended. In general, it is recommended to drink large amounts of water and carry out certain exercises to contract the muscles of the legs and thus stimulate the flow of blood.
There are also measures you can take to avoid a thrombosis forming:
- Keeping fit and exercising regularly
- Losing weight if you are overweight
- Eating healthily
- Stop smoking and drinking in excess
- If you sit for long periods, take regular breaks to walk around and stretch your legs
- Wear flight socks on long flights or car journeys (these can be bought from a pharmacy).
How is a thrombosis treated?
Treating a thrombosis depends on the patients overall health, age and medical history as well as the type of thrombosis detected. Treatment options include anti-coagulant medication (blood thinners), clot-dissolving medications, compression stockings and varicose vein removal. In patients with a thrombosis in the deep venous system of the leg (deep vein thrombosis), an emergency hospitalisation is required because if the clot detaches it, it could result in a pulmonary embolism or stroke.
