

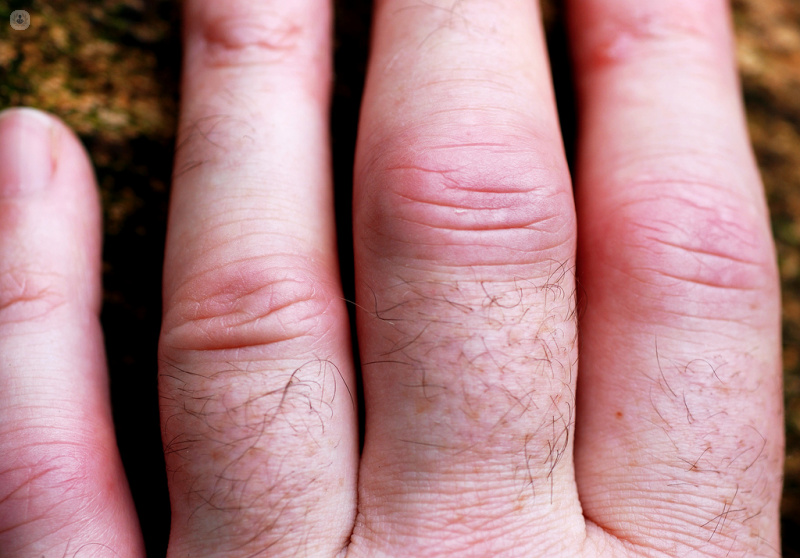
What are rheumatic diseases?
Rheumatic diseases are a group of diverse diseases of non-traumatic origin, which mainly affect the musculoskeletal system, such as joints, bones, muscles, tendons and ligaments. However, they can also affect other organs or systems.
There are more than 200 known rheumatic diseases. Some examples include:
- Arthritis – conditions causing inflammation of the joints. There are many forms of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout.
- Arthrosis
- Bursitis
- Giant cell arteritis
- Lupus
- Osteoporosis
- Polymyalgia rheumatica
What are the symptoms of rheumatic diseases?
The symptoms vary according to the person and the pathology. However, the most frequent symptoms are:
- Pain, often becoming chronic pain
- Heat, redness and swelling in the joints, especially in the case of rheumatoid arthritis
- Stiffness of the joints, particularly in the morning
- Fatigue, tiredness, feeling of weakness and lack of energy
- Sleep alterations
- General malaise
- Fever
- Muscle contractions
- Tingling and burning near the joint
- Loss of function of one or more joints
- Limited mobility
In addition, certain rheumatic diseases can cause other symptoms in various organs or systems, such as the skin (spots or wounds), the kidneys (blood in the urine), the eyes (loss of vision), the lungs or the heart (chest pain or shortness of breath).
Causes of rheumatic diseases
There are a number of factors that can cause rheumatic diseases. These include:
- Autoimmune – the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, e.g. rheumatoid arthritis
- Degeneration (due to natural wear and tear, old injuries, stress on joints due to weight, etc.), e.g. osteoarthritis
- Genetics – some people may be predisposed to rheumatic diseases due to their genes.
- Infections, e.g. rheumatic fever
Can rheumatic diseases be prevented?
Rheumatic diseases cannot be prevented with 100% certainty; however some of the associated risk factors can be avoided. It is recommended to protect the joints from excessive efforts and repetitive movements, and it is also important to maintain a healthy body weight to reduce stress on the joints.
Early diagnosis is very important, since it can prevent the worsening of symptoms.
What is the treatment?
The treatment of rheumatic diseases depends on the specific condition, but may include one or a combination of the following:
- Rest
- Moderate exercise
- Healthy diet
- Physiotherapy
- Insoles, knee braces, and other orthopaedic devices
- Painkillers, anti-inflammatories, and other medications as prescribed by the doctor
- Surgery
