

What is a pulmonary nodule?
Pulmonary nodules are spots on the lungs, which usually are no larger than 3cm in diameter. In most cases, they are benign and do not represent cancer. A pulmonary nodule will usually show on a chest x-ray or a CT scan. They can appear as individual nodules, or you may have several. If a pulmonary nodule is cancerous, they are usually larger than 3cm and may be irregular in shape.
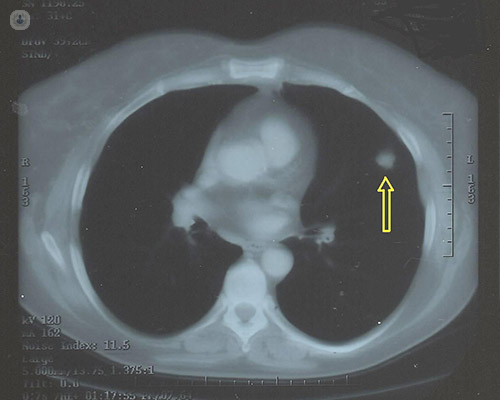
Prognosis of a pulmonary nodule:
Benign pulmonary nodules are more likely to be non-cancerous is you are a non-smoker, you are less than 40 years of age and the nodule is less than 3cm. If the nodule is confirmed as being cancerous, if there is just one nodule it is likely that the lung cancer is in earlier stages. However, a cancerous pulmonary nodule could be indicative of a metastasis from cancer that originated elsewhere in the body. This will mean a later stage cancer which will be treated accordingly.
Symptoms of a pulmonary nodule:
Pulmonary nodules are generally symptomless and you may have had a pulmonary nodule on your lung for months or years. If the nodules are cancerous, you may be experiencing symptoms related to the type of cancer in question, such as a cough and difficulties breathing.
Medical tests to diagnose a pulmonary nodule:
A chest x-ray or CT scan will usually indicate a pulmonary nodule, which may be performed if you have visited the doctor for respiratory symptoms or illness, such as a persistent cough. Once identified, your medical history will be assessed and whether you smoke or not. To determine if a nodule is cancerous a biopsy can be taken which can be carried out as a bronchoscopy or a needle biopsy. A PET scan may be performed to indicate whether the cells making up the nodule are dividing quickly, which would indicate cancer. Blood tests may also be carried out.
What are the causes of a pulmonary nodule?
Generally a benign pulmonary nodule will develop as a result of inflammation or scarring on the lungs. The following can cause this:
- Infections (e.g. tuberculosis)
- Neoplasms (abnormal growths that can be cancerous or non-cancerous)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
- Lung cancer
- Metastatic tumours
Can pulmonary nodules be prevented?
You can reduce the risk of pulmonary nodules forming by quitting smoking.
Treatments for a pulmonary nodule:
If the pulmonary nodule is benign, you will be advised to have regular check-ups to track any growth or change in the nodule. Sometimes a benign nodule can be removed surgically. If the pulmonary nodule is cancerous, cancer treatment will start and surgery will be considered to remove the cancerous growth.
Which type of specialist treats pulmonary nodules?
A pulmonary and respiratory medicine specialist would treat pulmonary nodules.
