

What is patellar tendonitis?
The patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap to the tibia, works with the muscles in the front of the thigh to extend the knee and allow running, jumping, walking, etc. Patellar tendonitis (also known as jumper's knee) is when this tendon is injured or overloaded.
This condition is more common in athletes whose sport involves frequent jumping, such as basketball and volleyball. However, non-athletes can also develop patellar tendonitis.
Prognosis:
Patellar tendonitis is not usually a serious injury, but it must be treated correctly so that it does not lead to anything else or long-term problems.
Symptoms of patellar tendonitis:
The main symptom of patellar tendonitis is pain, and may occur during physical activity or after intense training; it may worsen to the point of making it difficult to practice sports; or may make daily movements (such as climbing stairs) difficult. There may also be stiffness in the knee, pain when bending, or weakness in the leg.
Medical tests for patellar tendonitis:
The following tests are usually used to diagnose patellar tendonitis:
- MRI scan : a test that uses magnetic waves to make detailed pictures of the area which may show changes in the tendon
- Ultrasound: this uses sound waves to create a picture of the knee and show possible tears of the tendon.
- X-ray : to help exclude other bone problems related to the knee pain.
What causes patellar tendonitis?
Patellar tendonitis is usually caused by repeated stress on the patellar tendon. This causes tears in it that increase over time causing pain, inflammation and weakening of the tendon.
Can patellar tendonitis be prevented?
Different steps can be taken to try to prevent patellar tendonitis, such as:
- Strengthen muscles with exercise
- Improve your technique when playing sports
- Not exercising when suffering from pain
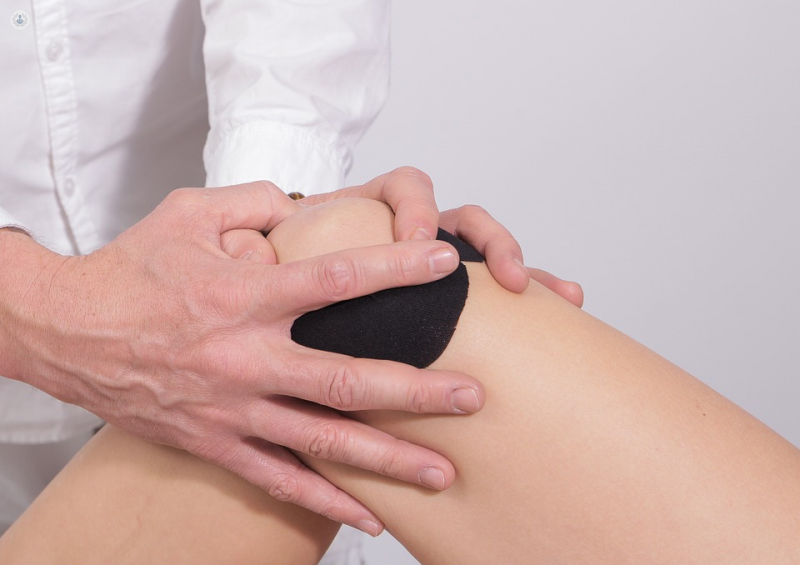
Treatments for patellar tendonitis:
Treatment usually begins with physical therapy to stretch and strengthen the muscles around the knee. A strap may also be applied to the patellar tendon that puts pressure on it and helps to distribute strength, relieving pain. Medications are also prescribed, corticosteroids and surgery is the last option.
Which specialist treats you?
An orthopaedic surgeon would treat cases of patellar tendonitis.
