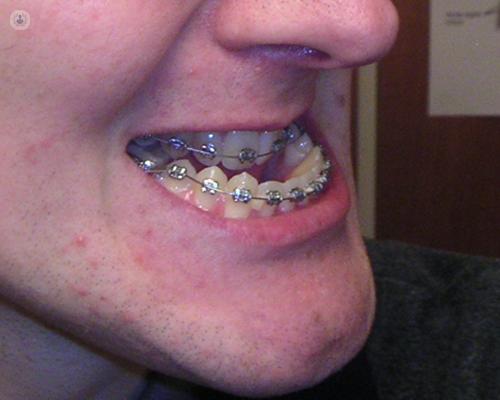
What is orthognathic surgery?
Orthognathic surgery aims to correct the position of the maxillary bone and jaw. This type of surgery can correct malocclusion (your bite) and other maxillofacial deformities. Often the results of orthognathic surgery will change the facial appearance.
The types of corrective surgery are:
- Mandibular advancement – when the lower teeth and chin are behind the rest of the face (this appears as an overbite and is also called a ‘weak chin’).
- Closure of an open bite – when the upper and lower teeth do not contact when closing the mouth and leave a space.
- Correcting protruding lower jaw – when the lower jaw juts out, beyond the upper jaw (this appears as an underbite).
- Correcting mandibular asymmetry – when the chin and teeth are diverted to one side, appearing wonky.
Orthognathic surgery may also be performed to treat the following problems:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty chewing or biting
- TMJ pain and headaches
- Wearing of the teeth
- Mouth breathing
- Sleep apnoea
- Facial injuries or birth defects
Why is orthognathic surgery done?
The objective of orthognathic surgery is to correct the position of the facial bones to improve jaw function and the appearance of the face. Orthognathic surgery will often be accompanied with orthodontic treatments, such as braces.
What does orthognathic surgery consist of?
Orthognathic treatment usually takes 2-3 years and will often begin with orthodontic treatment to move your teeth, usually using braces. Usually after 12-18 months of orthodontic treatment, jaw surgery will be performed. After this, orthodontic treatment is continued for another 6-9 months. Jaw surgery may focus on the upper or lower jaw, or in some cases, both. As the surgery is performed inside the mouth, you will not have visible scarring on your face. Once the jaw is repositioned, it is held in place with screws and plates, placed underneath the gums.
Preparation for orthognathic surgery:
Before surgery you will meet with the surgeon to discuss any allergies and medications you take. You will also have a pre-surgery blood test to ensure you are fit for surgery. If you are a smoker, you will need to quit before surgery as this will slow down recovery and increase the risk of infection following surgery.
Other preparation required before orthognathic surgery includes:
- Stockpiling liquid foods (e.g. soup, meal-replacement drinks and milk)
- Acquiring a food blender so that food can be liquidised and eaten more easily
- Arrange time off work and other responsibilities (you will usually need up to 4 weeks off)
Aftercare:
Following orthognathic surgery, you will usually stay in hospital for one night, after which you can return home. You will need 2-4 weeks off work or school, but complete healing can take up to 9 months. Your face will be swollen after surgery, but this improves within 2-3 weeks. You should start eating and drinking after surgery, eating soft foods (e.g. soup, smoothies and yoghurts) for the first couple of weeks. You should avoid hard foods for up to 6 weeks following surgery. It is also recommended that you use a soft-bristled toothbrush after surgery. You can expect to have a follow-up appointment 2-3 weeks after surgery.