

What is a lung biopsy?
A lung biopsy is a medical procedure performed to check lung tissue for disease or cancer. The procedure uses images to detect any abnormalities in the lung tissue, and then a small sample is removed for examination under a microscope.
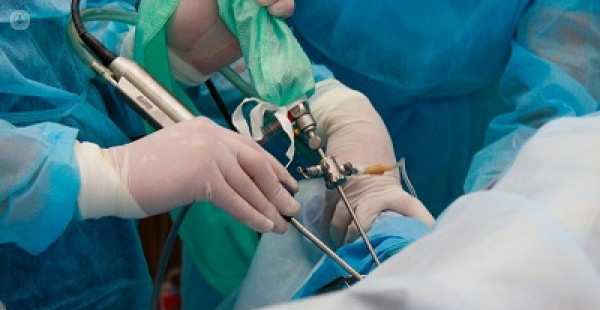
What does a lung biopsy involve?
The procedure lasts for around 30 to 60 minutes. An imaging system may be used to visualise and identify the area chosen for the biopsy. You sit on a table with your arms outstretched, while a sedative is administered and medication is injected for localised pain. A small incision is then made in the skin, through which the needle is inserted for the biopsy, to remove a sample of lung tissue. Once the procedure is complete, the needle is removed and pressure is applied to the affected area to stop any bleeding. A bandage is then applied. After the lung biopsy, a chest x-ray is performed, and the sample obtained is sent to a laboratory for a thorough examination to determine whether any disease or pathology is present.
Why would a lung biopsy be performed?
A lung biopsy should be performed when there is an abnormality in the area near the lung. The main aim of a lung biopsy is to rule out cancer. The procedure is performed if abnormalities have appeared in other tests, such as a chest x-ray or chest CT scan.
Preparing for a lung biopsy:
Before seeing the specialist for the procedure, you need to follow some guidelines. For example, do not eat anything for 6 to 12 hours before the procedure, do not take aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, or blood thinners such as warfarin in the days prior to the biopsy. If you have any questions about taking medication, you should consult your specialist.
What do you feel during the biopsy?
You will be given an anaesthetic to reduce the pain. However, as soon as the biopsy needle touches the lung, you will feel pressure and pain that may last for a few moments.
Meaning of abnormal results:
Abnormal results from a lung biopsy may indicate the following diseases or pathologies:
- A viral, bacterial, or fungal lung infection
- The presence of cancer cells, indicating lung cancer, or mesothelioma or pneumonia.
