

What is Hodgkin's disease?
Hodgkin's disease or Hodgkin lymphoma is a type of lymphoma, a cancer that originates in white blood cells or lymphocytes (defence cells of the immune system). It is a cancer of the lymphatic system, which is a network of organs, lymph nodes, ducts and lymphatic vessels that produce lymph and transport it from the tissues to the bloodstream, which is essential for the immune system.
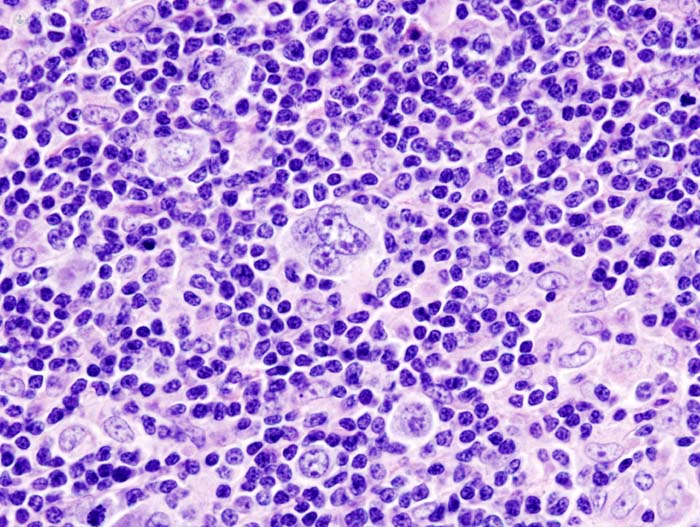
In Hodgkin lymphoma uncontrolled atypical lymphoid cells, called Reed-Sternberg, cause enlargement of the lymph nodes in a particular area, progressively movinf to other nearby areas, such as the spleen or bone marrow. Although Hodgkin’s disease can originate almost anywhere, it usually appears in the lymph nodes in the upper part of the body: chest, neck and armpits.
Hodgkin lymphoma is rare, accounting for less than 1% of all new cancer cases in the UK. However, incidence rates have increased over the last decade, and there are around 2,100 new cases every year. It affects men more than women
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Hodgkin lymphoma can be divided into two main types:
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma: the most common type (80% of cases), divided into the following:
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma rich in lymphocytes (10%)
- Hodgkin lymphoma with nodular sclerosis. This is the most frequent type (55%), affecting, above all, adolescents and young adults.
- Hodgkin lymphoma with mixed safety (16%)
- Hodgkin lymphoma with lymphocytic depletion. Common in patients with human immunodeficiency (HIV) (1%)
- Nodular lymphocytic predominance (20%)
What are the symptoms?
The most prevalent symptom of Hodgkin lymphoma is a generally painless swelling which appears in the neck, armpit, or groin. The swelling, while not painful, can ache. It is caused by an excess of lymphocytes collecting in one of the lymph nodes. Swollen lymph nodes, however, are not generally an indication of Hodgkin lymphoma, as the lymph nodes swell often in response to infection.
Other symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma include:
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
- A cough that won’t go away
- Feeling breathless
- Skin all over the body itching
- High temperature / fever
Certain symptoms may appear depending on the lymph nodes affected.
Causes of Hodgkin's disease or why it occurs
The causes of Hodgkin's disease are currently unknown. However, it is considered that an infection related to the Epstein-Barr virus, such as glandular fever, contributes to its appearance in certain cases. Likewise, people with HIV are at greater risk than the general population as HIV weakens the immune system.
Can it be prevented?
The few known risk factors for Hodgkin lymphoma cannot be prevented, therefore the condition itself generally cannot be prevented. HIV infection is known to increase the risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma, so avoiding risk factors associated with HIV can limit the risk of Hodgkin lymphoma.
What is the treatment?
The treatment of Hodgkin's disease varies according to the extent of the lymphoma, but it is most commonly based on chemotherapy, or chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy. In very few cases, chemotherapy is combined with steroid medication.
The overall prognosis for Hodgkin lymphoma is generally good providing the right treatment is given, and if the condition is detected early enough. Most of those with Hodgkin lymphoma are cured.
