What is gynaecological cancer?
Gynaecological cancer refers to any cancer that occurs in any of the organs of the female reproductive system, which is located in the pelvic region below the stomach and between the hips.
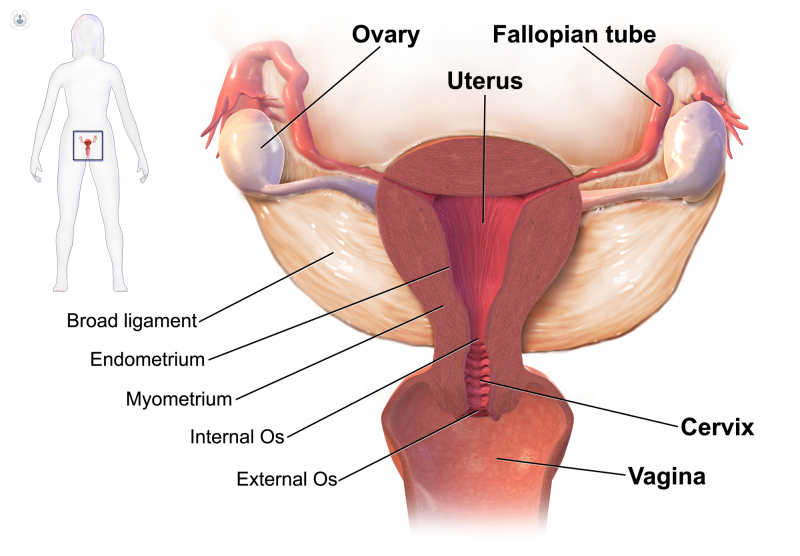
There are five types of gynaecological cancer, differentiated by location:
- Cervical cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Uterine cancer
- Vaginal cancer
- Vulvar cancer
Symptoms of gynaecological cancer
Each type of gynaecological cancer has its own signs, symptoms and risk factors:
Cervical cancer:
- Bleeding between periods
- Abundant vaginal discharge with small amounts of blood
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Abdominal pain and discomfort in the lower back
Ovarian cancer:
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen, similar to indigestion
- Pelvic pain
- Anaemia and weight loss
- Fatigue, loss of appetite
- Increased body hair due to hormonal disturbances
Uterine cancer:
- Bleeding between periods
- Abundant vaginal discharge with blood
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
Vaginal cancer:
- Bleeding between periods
- Back and/or pelvic pain
- Pain while urinating
- Small lumps in the vagina
Vulvar cancer:
- Burning sensation or bleeding in the vulva
- Colour is more reddish or paler than usual
- Appearance of warts or irritation similar to rash in the area
- Non-healing ulcers or lumps
- Pelvic pain during sexual intercourse or urination
What are the risk factors for gynaecological cancer?
Cervical cancer:
- HPV (human papilloma virus)
- Being a smoker
- Being HIV-positive
- Having sexual intercourse with different people continually
- Having given birth to more than three babies
Ovarian cancer:
- Being middle-aged or older
- Family history
- Certain genetic changes (mutations) can increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Mutations in the two breast cancer predisposition genes (BRCA1 and BRCA2) and those associated with Lynch syndrome increase the risk of ovarian cancer
- History of breast, uterine or colorectal cancer
- Having endometriosis
- Having no children or having difficulty conceiving
Uterine cancer
- Being older than 50 years
- Obesity
- Taking oestrogen-only (without progesterone) hormone replacement therapy during the menopause
- Having had difficulty conceiving
- Taking tamoxifen
- Family history of uterine, colon or ovarian cancer
Vaginal cancer:
- Vulvar cancer
- Having HPV (human papillomavirus)
- History of cervical cancer
- Weakened immune system
- Being a smoker
- Chronic burning sensation in the vulva


